4 mins to read
Classical Music
Author
Mahmudul
Published
December 21, 2024
0 comments
Join the Conversation
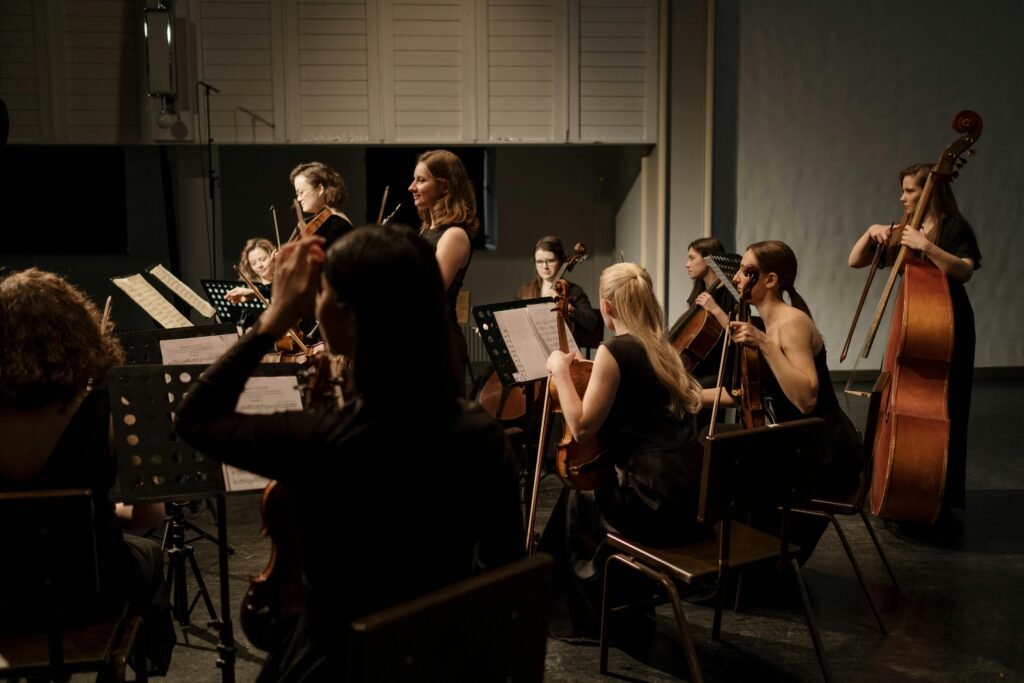
What is Classical Music?
Classical music refers to a style of music that adheres to established traditions and emphasizes complexity, balance, and emotional expression. It is primarily written in musical notation, allowing compositions to be preserved and performed consistently across generations.
-
- Features:
-
- Structured forms (e.g., sonatas, symphonies, concertos).
-
- Use of orchestral instruments (strings, brass, woodwinds, percussion).
-
- Written for ensembles, soloists, or vocal performances.
-
- Emphasis on melody, harmony, and formal structure.
-
- Features:
Classical music is not limited to a single era or style but refers to a tradition that began in the medieval period and continues to influence modern music.
Why is Classical Music Considered Timeless or Popular?
Classical music is often considered timeless due to its universal themes, technical brilliance, and enduring emotional resonance.
-
- Timeless Appeal:
-
- Universal human emotions such as love, sorrow, joy, and triumph are expressed in compositions.
-
- Pieces like Beethoven’s “Fifth Symphony” or Mozart’s “Requiem” continue to resonate with audiences.
-
- Timeless Appeal:
-
- Technical Mastery:
-
- Classical music requires precision and skill, making it both challenging and rewarding to perform.
-
- Technical Mastery:
-
- Cultural Influence:
-
- It has shaped modern music genres such as film scores, jazz, and rock.
-
- Classical melodies and techniques appear in contemporary music, advertising, and cinema.
-
- Cultural Influence:
-
- Accessibility:
-
- Advances in recording and performance technology have brought classical music to global audiences.
-
- Accessibility:
How Did Classical Music Start?
Classical music evolved as a formalized way of creating and preserving music in written form. It grew out of early religious and folk traditions.
-
- Medieval Period (500–1400):
-
- Roots in Gregorian Chant and liturgical music of the Christian Church.
-
- Introduction of polyphony (multiple simultaneous melodies).
-
- Medieval Period (500–1400):
-
- Renaissance Period (1400–1600):
-
- Music became more expressive and complex with the advent of harmony and counterpoint.
-
- Composers like Palestrina and Josquin des Prez emphasized vocal music.
-
- Renaissance Period (1400–1600):
-
- Baroque Period (1600–1750):
-
- Birth of opera, instrumental suites, and the concerto form.
-
- Key figures: Johann Sebastian Bach, George Frideric Handel, Antonio Vivaldi.
-
- Baroque Period (1600–1750):
When Did Classical Music Originate?
Classical music began to take form during the Medieval Period around 500 CE. However, the term “Classical Music” often refers to the period between 1750 and 1820 (known as the Classical Period). Over time, it has expanded to include earlier and later traditions.
Where Did Classical Music Originate From?
Classical music originated in Europe, particularly in regions influenced by the Christian Church. Over time, specific hubs of musical innovation emerged:
-
- Italy: Known for opera and sacred music.
-
- Germany and Austria: Central to symphonies and sonatas, home to composers like Bach, Mozart, and Beethoven.
-
- France: Developed unique contributions to ballet and Impressionist music.
-
- England: Notable for choral traditions and later Romantic compositions.
Who Are the Key Composers or Figures in Classical Music?
-
- Baroque Period (1600–1750):
-
- Johann Sebastian Bach: Master of counterpoint and fugues.
-
- George Frideric Handel: Famous for operas and oratorios, including “Messiah”.
-
- Antonio Vivaldi: Known for “The Four Seasons”.
-
- Baroque Period (1600–1750):
-
- Classical Period (1750–1820):
-
- Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart: Prolific composer known for operas, symphonies, and chamber music.
-
- Ludwig van Beethoven: Transitioned from Classical to Romantic styles with works like “Symphony No. 9”.
-
- Joseph Haydn: Father of the symphony and string quartet.
-
- Classical Period (1750–1820):
-
- Romantic Period (1820–1900):
-
- Franz Schubert: Known for lieder (German art songs) and symphonies.
-
- Frédéric Chopin: Virtuoso pianist, famous for piano nocturnes and preludes.
-
- Richard Wagner: Innovator of opera, known for “The Ring Cycle”.
-
- Romantic Period (1820–1900):
-
- 20th Century and Beyond:
-
- Igor Stravinsky: Revolutionary works like “The Rite of Spring”.
-
- Claude Debussy: Pioneer of Impressionist music, famous for “Clair de Lune”.
-
- Leonard Bernstein: Blended classical and modern elements, famous for “West Side Story”.
-
- 20th Century and Beyond:
What Are the Major Subgenres or Styles of Classical Music?
-
- Sacred Music:
-
- Includes masses, oratorios, and hymns.
-
- Example: Bach’s “Mass in B Minor”.
-
- Sacred Music:
-
- Opera:
-
- Combines vocal and instrumental music with dramatic storytelling.
-
- Example: Mozart’s “The Magic Flute”, Verdi’s “La Traviata”.
-
- Opera:
-
- Symphony:
-
- Large-scale orchestral works, often in four movements.
-
- Example: Beethoven’s “Symphony No. 5”.
-
- Symphony:
-
- Concerto:
-
- Features a solo instrument with orchestral accompaniment.
-
- Example: Vivaldi’s “The Four Seasons”.
-
- Concerto:
-
- Chamber Music:
-
- Written for small ensembles, like string quartets.
-
- Example: Haydn’s String Quartets.
-
- Chamber Music:
-
- Sonata:
-
- Works for solo instruments, often with piano accompaniment.
-
- Example: Beethoven’s “Moonlight Sonata”.
-
- Sonata:
-
- Ballet:
-
- Music composed for dance, often performed in theatrical settings.
-
- Example: Tchaikovsky’s “Swan Lake”.
-
- Ballet:
-
- Impressionism:
-
- Focuses on mood and atmosphere rather than strict form.
-
- Example: Debussy’s “Prélude à l’après-midi d’un faune”.
-
- Impressionism:
-
- Minimalism:
-
- Emphasizes repetition and simplicity.
-
- Example: Philip Glass’s “Glassworks”.
-
- Minimalism:
Conclusion
Classical music is an enduring art form that spans centuries and continues to inspire listeners and musicians worldwide. From its origins in Europe to its global influence, classical music encompasses a wide range of styles, composers, and innovations. By exploring its history, key figures, and subgenres, one can appreciate the timeless beauty and complexity of this remarkable musical tradition.